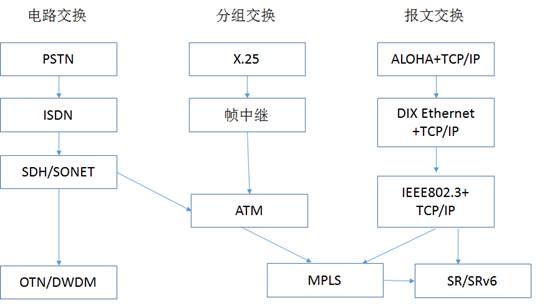
Ethernet is a networking technology that enables data communication over local area networks (LANs) and has become a standard in modern networking. Initially developed in the 1970s by Xerox Corporation, it has undergone significant evolution, resulting in various standards and speeds suitable for diverse applications.
Key Features
- Standard Protocol: Governed by the IEEE 802.3 standard, Ethernet ensures compatibility across different devices and manufacturers, making it universally adopted in both residential and commercial environments.
- Data Transmission: Ethernet uses a frame format to transmit data, which includes key components such as destination and source MAC addresses, a type/length field, and a payload section. This structure allows for efficient data encapsulation and transmission.
- Speed Variability: Ethernet technology supports a range of speeds, from the original 10 Mbps to modern standards like Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps), Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps), and multi-gigabit options (10 Gbps and beyond), catering to various network demands.
- Physical Media: Ethernet can operate over multiple physical media, including twisted pair cables (Cat5e, Cat6), coaxial cables, and fiber optics. This flexibility allows for different deployment scenarios based on performance and distance requirements.
- Collision Detection and Avoidance: Early Ethernet used Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) to manage data traffic. In modern switched Ethernet networks, collisions are minimized by using switches to provide dedicated connections, enhancing performance and reliability.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Ethernet networks are easily scalable, allowing for the straightforward addition of devices and accommodating network growth without extensive reconfiguration.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Advanced Ethernet standards incorporate QoS mechanisms to prioritize different types of traffic, ensuring that critical applications (like VoIP or video conferencing) receive the necessary bandwidth and latency considerations.
Applications
Ethernet is employed in a wide array of applications, including home networking, enterprise environments, data centers, and industrial settings. Its robustness, reliability, and high-speed capabilities make it a preferred choice for organizations aiming to build efficient and scalable networks.
In conclusion, Ethernet remains an ultimate networking solution, continuously adapting to evolving technology trends while retaining its foundational principles. Its versatility and reliability have solidified its status as a cornerstone of contemporary data communication.