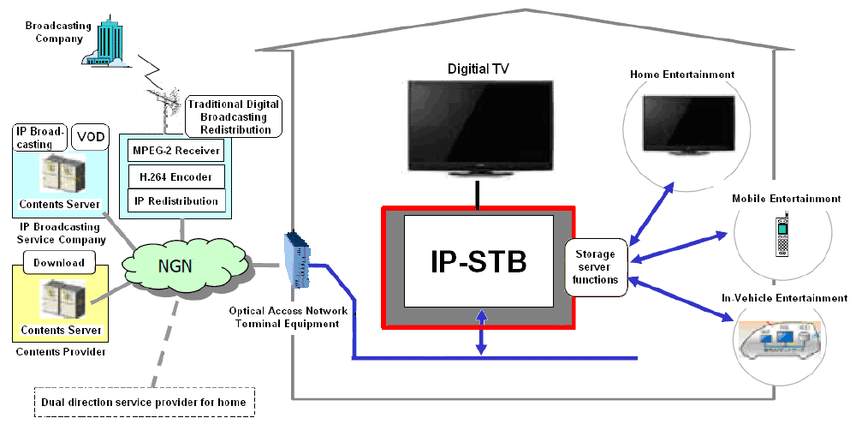
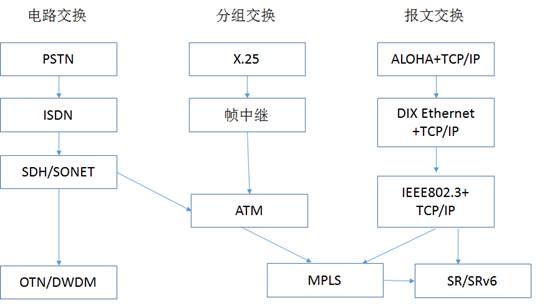
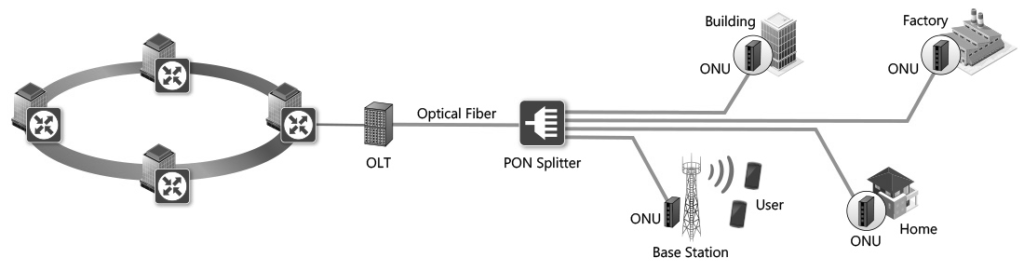
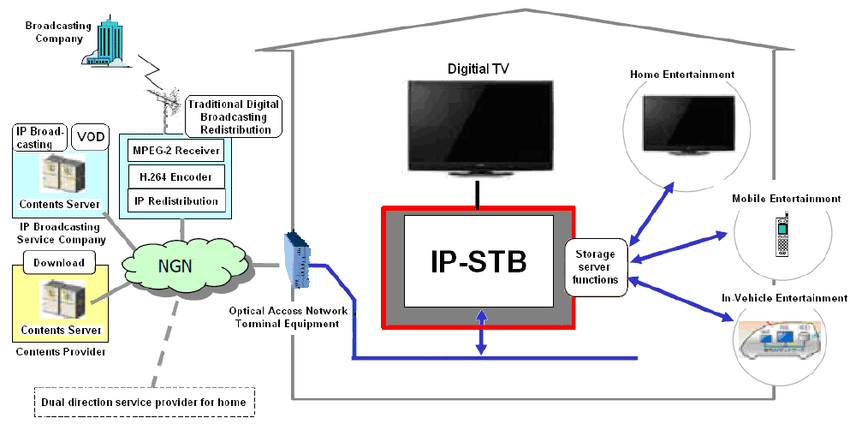
Ethernet Access Technologies
Ethernet access technology is a widely used method for connecting end-users to broadband networks. It is based on the Ethernet protocol, which has evolved to support various speeds and services. Here are some key aspects of Ethernet access technologies:
1. Overview of Ethernet Technology
Ethernet is a networking standard that defines how data packets are formatted and transmitted over a network. Originally designed for local area networks (LANs), it has been adapted for use in wide area networks (WANs) and access networks.
2. Types of Ethernet Access
- Fiber to the Home (FTTH): This technology provides high-speed internet access by extending fiber optic cables directly to residential homes. It offers very high bandwidth and is less susceptible to interference.
- Ethernet over Fiber (EoF): Utilizes fiber optic cables to transmit Ethernet frames over long distances. This method is commonly used in businesses to connect to service providers.
- Ethernet over Copper (EoC): Involves the use of traditional copper wiring (e.g., DSL or T1 lines) to deliver Ethernet services. While it has lower speeds compared to fiber, it is often easier and less expensive to deploy in existing infrastructures.
3. Benefits of Ethernet Access
- Scalability: Ethernet can easily scale from small local networks to large enterprise solutions.
- Cost-Effective: Deployment of Ethernet is generally less expensive compared to other access technologies, especially in urban areas where existing infrastructure can be leveraged.
- Flexibility: Ethernet supports various data rates and can be used for different services, including internet access, VoIP, and video streaming.
4. Challenges
- Distance Limitations: Traditional Ethernet over copper has distance limitations, affecting performance in rural areas.
- Interference: Copper-based solutions are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference, which can impact signal quality.
- Bandwidth Sharing: In shared Ethernet environments, bandwidth may be contested among multiple users, potentially affecting performance.
5. Future Trends
- Ethernet Passive Optical Networks (EPON): This technology combines Ethernet with passive optical networks to provide high-speed internet access, particularly in residential areas.
- Next-Generation Ethernet Standards: Continuous improvements in Ethernet standards are being developed to support higher speeds (e.g., 10G, 100G) and enhanced functionalities.
In summary, Ethernet access technologies provide a robust, scalable, and cost-effective solution for broadband connectivity, catering to both residential and business needs. As technology advances, Ethernet continues to evolve, offering higher speeds and better performance to meet increasing demand.